Dosing flexibility
Dosing for patients with primary HLH
Tailor Gamifant treatment to your patient's needs
Gamifant is administered1:
- By central or peripheral intravenous infusion over 1 hour twice a week (every 3-4 days)
- Until the patient no longer requires therapy for the treatment of primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), until hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is performed, or until unacceptable toxicity is reached
- If conditioning is required, Gamifant can be administered throughout conditioning until HSCT is successfully performed
- If primary HLH symptoms recur, Gamifant can be readministered
- Concomitantly with dexamethasone at a starting daily dose of at least 5 to 10 mg/m2 the day before Gamifant treatment begins
- Using a gamma-irradiated or ethylene oxide–sterilized, latex-free, polyvinyl chloride (PVC)-free syringe, or
- Using a non-PVC polyolefin infusion bag
Gamifant offers flexibility of dosing1
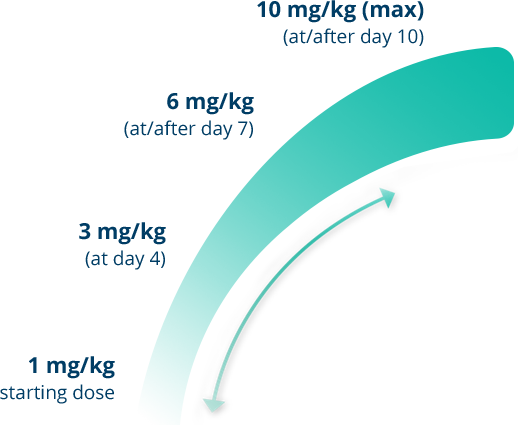
The recommended starting dose of Gamifant is 1 mg/kg.1
Gamifant can be incrementally titrated upward or downward according to the clinician's assessment of patient response. After the patient’s clinical condition is stabilized, decrease the dose to the previous level to maintain clinical response until HSCT.1
Dexamethasone can be tapered according to the judgment of the treating physician to help reduce the risk of overexposure. A steady reduction in dexamethasone dosage was achieved in the Gamifant pivotal trial.1
Drug interactions
The formation of CYP450 enzymes may be suppressed by increased levels of cytokines (such as interferon gamma [IFNγ]) during chronic inflammation. By neutralizing IFNγ, use of Gamifant may normalize CYP450 activities, which may reduce the efficacy of drugs that are CYP450 substrates due to increased metabolism. Upon initiation or discontinuation of concomitant Gamifant, monitor for reduced efficacy and adjust dosage of CYP450 substrate drugs as appropriate.
Response criteria for dose increase1After initiating Gamifant, monitor patients’ response to determine whether a dose increase may be needed based on clinical assessment of unsatisfactory improvement and one of the following | |
Fever | Persistence or recurrence |
Platelet Count |
|
Neutrophil Count |
|
Ferritin |
|
Splenomegaly | Any worsening |
Coagulopathy | Both D-dimer and fibrinogen must apply
|
Speak with a Gamifant representative
If you have questions about Gamifant or would like more information, please contact your Gamifant representative.
Target-mediated clearance
Gamifant exhibits target-mediated clearance dependent on IFNγ production, which can vary between and within patients as a function of time and can affect the recommended dosage.1
- The pharmacokinetics of emapalumab-lzsg were evaluated in healthy adult subjects and in patients with primary HLH1
- Gamifant steady-state is achieved by the seventh infusion when the IFNγ production is moderate. At high IFNγ production, steady-state is reached earlier due to a shorter half-life1
- The half-life of Gamifant is approximately 22 days in healthy subjects, and ranged from 2.5 to 18.9 days in patients with primary HLH1
Dosing flexibility is especially important given this variability, and dose adjustments may be needed to neutralize IFNγ concentrations in each patient.
The recommended starting dose of Gamifant is 1 mg/kg.1
- If the same clinical and laboratory criteria still apply after incremental titration, the dose of Gamifant may continue to increase to a maximum of 10 mg/kg1
- Titration should be based on clinical and lab parameters interpreted as unsatisfactory1
Identify the right dose of Gamifant with our Dosing Calculator.