Testing for primary HLH
Additional testing and CXCL9 in primary HLH
When it comes to treating primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), there’s no time to wait. Prior to receiving genetic testing results, other assessments can help you determine the likelihood of primary HLH so that you can initiate treatment as soon as possible.1

empty on purpose
Flow cytometry testing
Decreased levels of the following can help identify a genetic cause1
Perforin/granzyme B
Degranulation (CD107a) or T-cell degranulation
SLAM-associated protein (SAP) (for males)
XIAP protein (for males)
CD=cluster of differentiation; SLAM=signaling lymphocytic activation molecule; XIAP=X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein.
Flow cytometry for perforin expression and CD107a have high specificity for identifying primary HLH1
Ancillary testing1
Quantitative viral PCRs
EBV, CMV, adenovirus, HSV 1, HSV 2, etc
CT of chest, abdomen, and neck
Testing for tick- or mosquito-borne diseases
PET-CT
followed by lymph node biopsy to evaluate for lymphoma
MRI of brain
Lyme disease
CMV=cytomegalovirus; CT=computed tomography; EBV=Epstein-Barr virus; HSV=herpes simplex virus;
MRI=magnetic resonance imaging; PCR=polymerase chain reaction; PET=positron emission tomography.
These tests can help eliminate other conditions and/or define treatable underlying triggers for HLH1-4
CXCL9
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 (CXCL9) is a type of cytokine released almost exclusively by interferon gamma (IFNγ)-activated macrophages.5 The primary function of CXCL9 is to attract T cells into inflamed tissues.6
empty on purpose
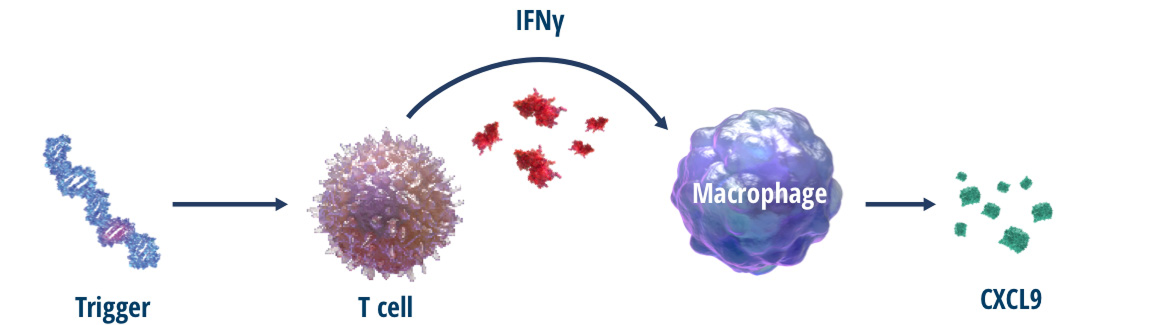
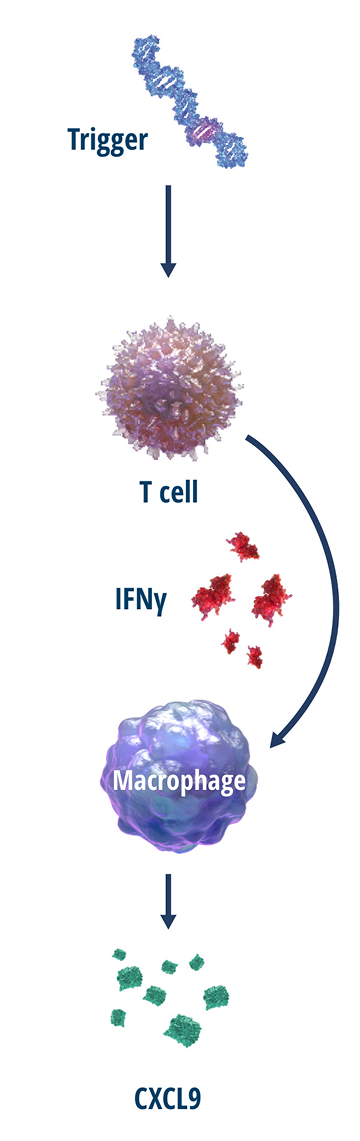
CXCL9 production is induced predominantly by IFNγ.5 Evidence suggests CXCL9 is a potential biomarker for IFNγ activity.7
CXCL9 testing sites
There is growing recognition of testing for CXCL9 as a biomarker for IFNγ activity.7 The following organizations offer CXCL9 testing to help with identifying primary HLH:
Machaon Diagnostics | |
Website | |
Turnaround time | STAT: <24 hours |
Lab hours | 24/7 |
Phone | 1-800-566-3462 |
Fax | 510-839-6153 |
Cincinnati Children’s Hospital | |
Website | |
Turnaround time | 4 days |
Lab hours | Mon-Fri, 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM (ET) |
Phone | 513-636-4685 |
Fax | 513-636-3861 |
This is not an exhaustive list of labs offering CXCL9 testing. Please check for the availability of this test within your own institution prior to contacting these sites.
Other tests1,8
In the absence of an underlying cause, such as malignancy, these tests can be useful for identifying the typical features of primary HLH.1,8
- Complete blood counts
- Ferritin
- ALT, bilirubin
- IL-18
- Fibrinogen/coagulation tests
- Triglycerides (fasting)
- sCD25
ALT=alanine transaminase; IL-18=interleukin-18; sCD25=soluble cluster of differentiation 25.